About SDG Tracker
SDG 1: No Poverty
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 2: Zero Hunger
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
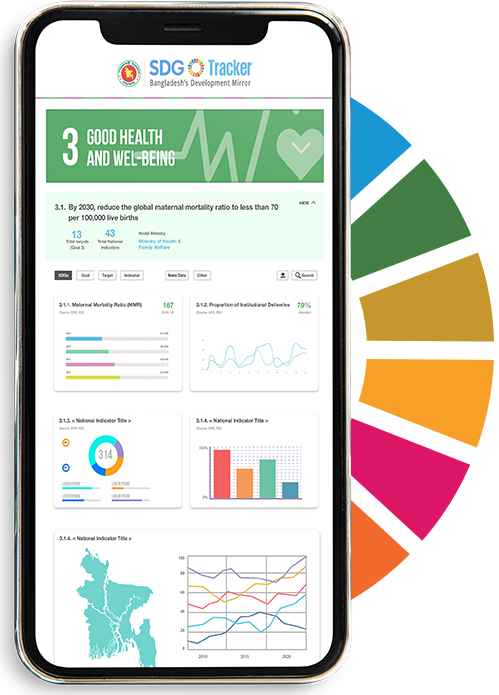
SDG 3: Good health and well-being
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 04: Quality Education
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 05: Gender Equality
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 06: Clean water and Sanitation
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 07: Affordable and Clean Energy
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 08: Decent work and Economic growth
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 09: Industry, Innovation and Infrastructure
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 10: Reduced Inequalities
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 11: Sustainable Cities and Communities
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 12: Responsible Consumption and Production
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 13: Climate Action
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 14: Life Below Water
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 15: Life on Land
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.
SDG 16: Peace, Justice and strong Institutions
Eradicating poverty in all its forms remains one of the greatest challenges facing humanity. While the number of people living in extreme poverty dropped by more than half between 1990 and 2015 – from 1.9 billion to 836 million – too many are still struggling for the most basic human needs. Globally, more than 800 million people are still living on less than US$1.25 a day, many lacking access to adequate food, clean drinking water and sanitation. Rapid economic growth in countries like China and India has lifted millions out of poverty, but progress has been uneven. Women are more likely to live in poverty than men due to unequal access to paid work, education and property. Progress has also been limited in other regions, such as South Asia and sub-Saharan Africa, which account for 80 percent of those living in extreme poverty. New threats brought on by climate change, conflict and food insecurity, mean even more work is needed to bring people out of poverty. The SDGs are a bold commitment to finish what we started and end poverty in all forms and dimensions by 2030. This involves targeting the most vulnerable, increasing access to basic resources and services and supporting communities affected by conflict and climate-related disasters.


